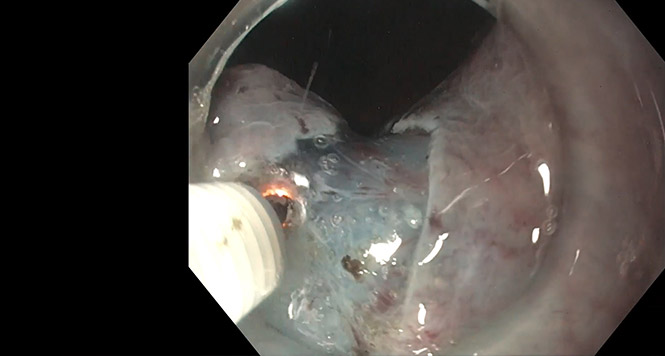
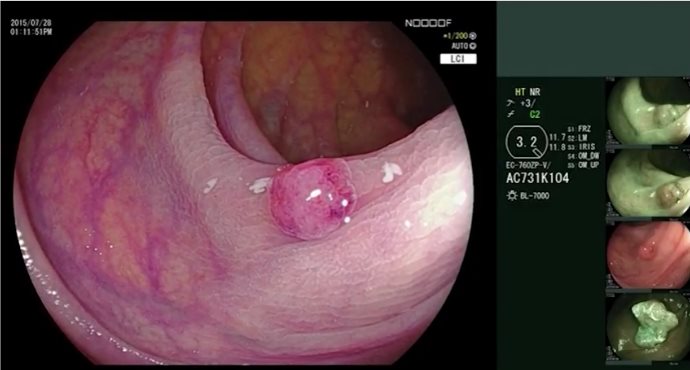
In this case, a 65-year-old woman presents with a recurrence of a polyp previously treated with endoscopic mucosal resection. The biopsy and the endoscopic evaluation
polyps
polyps
Rectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Polyp Classification: BASIC
Basic (BLI Adenoma Serrated International Classification) Classification for colorectal polyp characterization with blue light imaging
Cold Snare on the Rise?
Cold snare resection has been established in diminutive polyps (up to 5 mm) as being at least as safe and partially more effective than biopsy
Paris Classification: Early Barrett Cancers
In the following, examples for superficial/early Barrett lesions of the esophagus are shown. Here, flat and sessilelesions are predominant, pedunculated tumors are rare. Sessile tumor
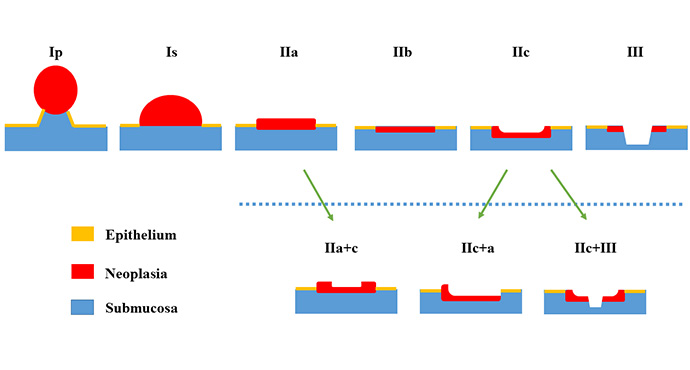
Paris Classification: Early Colorectal Cancers
The Paris classification for superficial / early tumors should be part of a standard terminology for endoscopic assessment. This classification applies to the entire gastrointestinal
Optimizing the adenoma detection rate – a never-ending story? Or does the outcome quality depend on the follow-up?
The adenoma detection rate (ADR) is the holy grail of quality assurance in colonoscopy. It is the main parameter for outcome quality — or more
Paris Classification Early Cancer
Endoscopic treatment for early carcinoma in the gastrointestinal tract has in the meantime become evidence-based and has been incorporated into national and international guidelines
Paris Classification: Early Squamous Cell Cancers Esophagus
Examples of superficial/early squamous cell lesions in the esophagus are presented below. In the esophagus, flat lesions are predominant in the early tumors, and polypoid
Paris Classification: Early Gastric Cancer
Examples of superficial/early gastric tumors are shown below. In the stomach, flat lesions are predominant, often as combined lesions with a central depression (IIa+c). Sessile
Endocuff Vision® versus wide-angle endoscope: small attachment – big effect
The wide-angle colonoscope provides a field of view up to 235 degrees, thanks to a lens system featuring forward viewing (147 degrees) and also side
Polyp Classification: NICE
The NICE (NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic) Classification is based on narrow-band images of colon polyps. The classification uses staining, vascular patterns, and surface patterns to
Rectal NET Tumors
Unclear smaller polyps in the rectum may represent a pitfall — if they do not look like perfectly typical hyperplasia or small adenomas, then carcinoids
Endoscopic diagnosis of colon polyps using the NICE classification: initial experience with BLI and LCI
The new generation of the Fujifilm electronic endoscopy system allows virtual chromoendoscopy alongside zoom endoscopy. Blue laser imaging (BLI), like narrow-band imaging (NBI), allows further