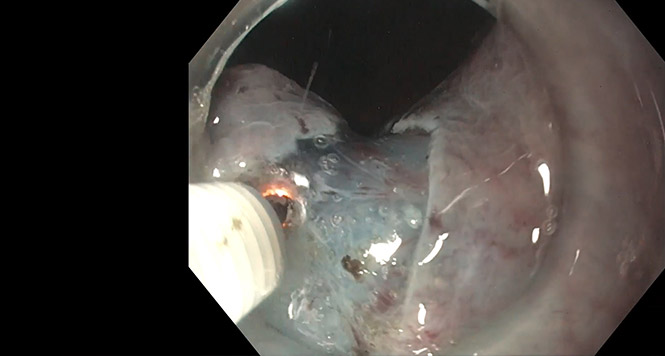
Polyp Classification: NICE
The NICE (NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic) Classification is based on narrow-band images of colon polyps. The classification uses staining, vascular patterns, and surface patterns to distinguish between hyperplastic and adenomatous colon polyps. Although it is linked to the Olympus company’s endoscopes, similar differential-diagnostic approaches have also been reported for devices manufactured by other companies. Clinically, the classification is used for small polyps (< 5 mm or < 10 mm).
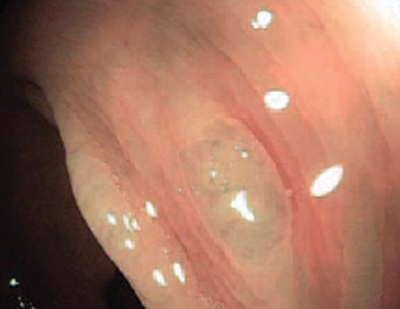
Type 1 — characteristic for hyperplastic polyp
Vessels: lighter than or similar to the surroundings
Gefäße: small vessels or a sparse network, with no recognizable pattern
Surface: circular pattern with small dots — pattern with a darker area in the center, surrounded by lighter mucosa
Further examples:
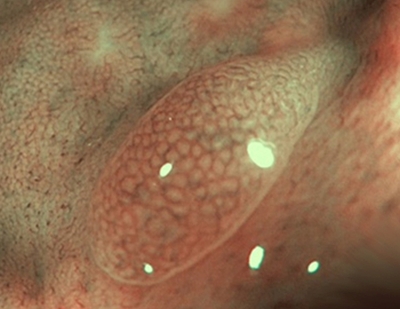
Type 2 — characteristic for adenoma
Color: darker (browner) than the surroundings
Vessels: a lighter area in the center, surrounded by thicker brown vessels
Surface: oval, tubular, gyrate — presence of tubuli, linear or bundled, light area in center, surrounded by brown vessels
Further examples:
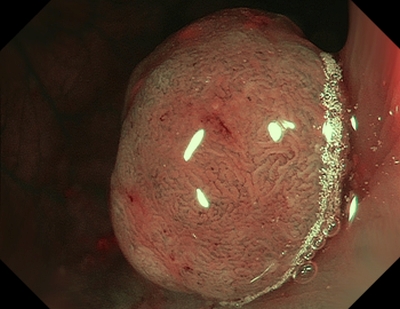
Type 3 — characteristic for malignancy (SM)
Color: darker than the surroundings, brownish, sometimes with lighter patches
Vessels: areas with interrupted or absent vessels
Surface: amorphous or no surface pattern
NICE Classification
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Same or lighter than background | Brown relative to background (verify color arises from vessels) | Brown to dark brown relative to background; sometimes patchy whiter areas |
| Vessels | None, or isolated lacy vessels may be present coursing across the lesion | Brown vessels surrounding white structures* | Has area(s) of disrupted or missing vessels |
| Surface patterns | Dark or white spots of uniform size, or homogeneus absence of pattern | Oval, tubular or branched white structures* surrounded by brown vessels | Amorphous or absent surface pattern |
| Most likely pathology | Hyperplastic | Adenoma** | Deep submucosal invasive cancer |
| Sample Image | 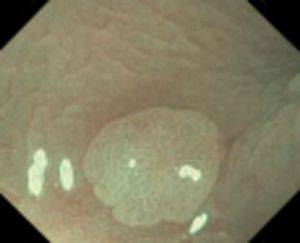 |
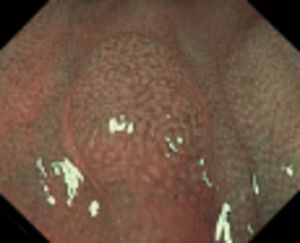 |
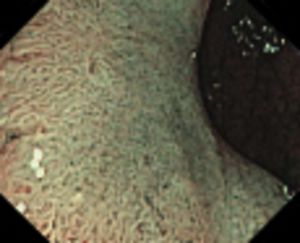 |
| This classification can be applied using colonoscopes both with or without optical (zoom) magnification. * These structures (regular or irregular) may represent the pits and the epithelium of the crypt opening. ** Type 2 consists of Vienna classification types 3, 4 and superficial 5 (all adenomas with either low or high grade dysplasia, or with superficial submucosal carcinoma). The presence of high grade dysplasia or superficial submucosal carcinoma may be suggested by an irregular vessel or surface pattern, and is often associated with atypical morphology (e.g., depressed area). |
|||
References
- Hewett DG, Kaltenbach T, Sano Y, Tanaka S, Saunders BP, Ponchon T, Soetikno R, Rex DK. Validation of a simple classification system for endoscopic diagnosis of small colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging. Gastroenterology. 2012 Sep;143(3):599-607.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 May 15.
- Rex DK, Kahi CJ, Michael O’Brien M, et al.: The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy PIVI on real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 2011; 73:419-422
- McGill SK, Evangelou E, Ioannidis JP, Soetikno RM, Kaltenbach T. Narrow band imaging to differentiate neoplastic and non-neoplastic colorectal polyps in real time: a meta-analysis of diagnostic operating characteristics. Gut. 2013 Dec;62(12):1704-13. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303965. Epub 2013 Jan 7
- Nagorni A, Bjelakovic G, Petrovic B. Narrow band imaging versus conventional white light colonoscopy for the detection of colorectal polyps. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD008361. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008361.pub2.
- van den Broek FJ, Reitsma JB, Curvers WL, Fockens P, Dekker E. Systematic review of narrow-band imaging for the detection and differentiation of neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions in the colon (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009 Jan;69(1):124-35. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.09.040.
- Wanders LK, East JE, Uitentuis SE, Leeflang MM, Dekker E. Diagnostic performance of narrowed spectrum endoscopy, autofluorescence imaging, and confocal laser endomicroscopy for optical diagnosis of colonic polyps: a meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013 Dec;14(13):1337-47. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70509-6. Epub 2013 Nov 13
- Rastogi A, Bansal A, Wani S, et al. Narrow-band imaging colonoscopy–a pilot feasibility study for the detection of polyps and correlation of surface patterns with polyp histologic diagnosis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:280-6. Epub 2007 Dec 26.
- Rastogi A, Keighley J, Singh V, et al. High accuracy of narrow band imaging without magnification for the real-time characterization of polyp histology and its comparison with high-definition white light colonoscopy: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2422-30. Epub 2009 Jul 7.
- Rastogi A, Early DS, Gupta N et al.. Randomized, controlled trial of standard-definition white-light, high-definition white-light, and narrow-band imaging colonoscopy for the detection of colon polyps and prediction of polyp histology. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;74:593-602
- Gupta N, Bansal A, Rao D, et al. Accuracy of in vivo optical diagnosis of colon polyp histology by narrow-band imaging in predicting colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:494-502. Epub 2011 Oct 26
- Hassan C, Pickhardt PJ, Rex DK. A resect and discard strategy would improve cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:865-9, 869.e1-3. Epub 2010 Jun 1.
- Ignjatovic A, East JE, Suzuki N, er al. Optical diagnosis of small colorectal polyps at routine colonoscopy (Detect InSpect ChAracterise Resect and Discard; DISCARD trial): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:1171-8. Epub 2009 Nov
- Wallace MB, Kiesslich R. Advances in endoscopic imaging of colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:2140-50.
- Ladabaum U, Fioritto A, Mitani A, et al.: Real-Time Optical Biopsy of Colon Polyps With Narrow Band Imaging in Community Practice Does Not Yet Meet Key Thresholds for Clinical Decisions. Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan;144(1):81-91. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.054. Epub 2012 Oct 3.
- Schachschal G, Mayr M, Treszl A, Balzer K, Wegscheider K, Aschenbeck J, Aminalai A, Drossel R, Schröder A, Scheel M, Bothe CH, Bruhn JP, Burmeister W, Stange G, Bähr C, Kießlich R, Rösch T. Endoscopic versus histological characterisation of polyps during screening colonoscopy.Gut. 2014 Mar;63(3):458-65. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304562. Epub 2013 Jun 28.