Those at high risk or with a prior history of esophageal squamous cell cancer (SCC) are recommended to undergo screening or surveillance using dye-based chromoendoscopy.
NBI
NBI
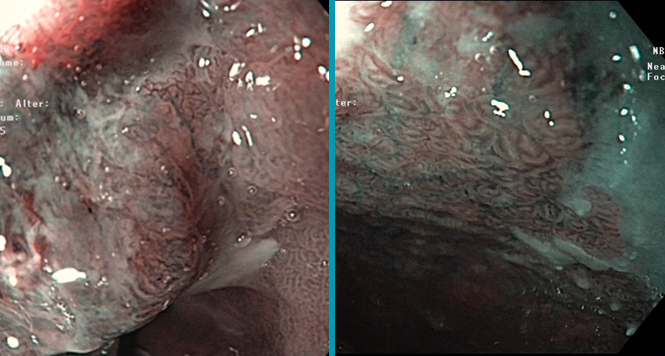
Narrow-Band Imaging Is a Good Screening Modality for Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer for Expert and General Endoscopists
Endoscopic Features for Recognizing Buried Barrett’s Esophagus
Buried Barrett’s esophagus (BE) mucosa, or subsquamous intestinal metaplasia, is defined as intestinal metaplasia that is present under a lining of endoscopically intact squamous epithelium.
Stomach: Light Blue Crest Sign for Intestinal Metaplasia
Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia is a risk factor of intestinal-type gastric cancer, but WLI was not adequate to detect IM of stomach. NBI system with and
BING Classification Early Barrett Neoplasia
Multimodal therapy for early Barrett’s neoplasias, has become established as the standard therapy and is set out in national and international guidelines. These dysplastic lesions
WASP classification – optical diagnosis of polyps <10mm
Recently sessile serrated lesions (SSLs) have been recognized as another important precursor lesion to CRC. SSLs are thought be responsible for 15–30% of colorectal cancer.
Polyp Classification: NICE
The NICE (NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic) Classification is based on narrow-band images of colon polyps. The classification uses staining, vascular patterns, and surface patterns to