Sequenzen:

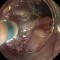
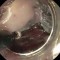
In this 71-year-old patient in whom a squamous-cell carcinoma had been diagnosed at an outside institution, areas of reddish discoloration with whitish surface spots stand out more clearly from their surroundings on narrow-band imaging. The surface is also bumpy and irregular. Before endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), marks are placed outside the lesion, at a distance of at least 3–4 mm from the visible margin of the tumor.

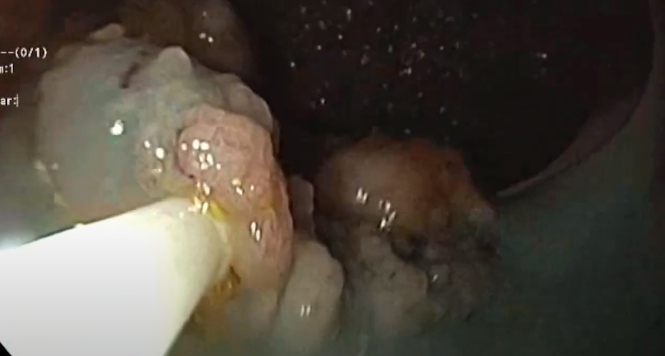
After the first incision using the “dual knife,” submucosal connective tissue that is rich in blood vessels appears. Dissection is carried out using the extensible and retractable knife, with cutting current or mixed current, or with coagulation current for the vessels. When dissection is complete, the entire lesion with the incision around it is visible.

The final steps of the dissection on the lower margin are also carried out with the IT knife. On the inhomogeneous resection surface, residual vessels and small superficial muscle defects are closed with clips. The mounted specimen, with its margins macroscopically tumor-free, is inspected. Histological analysis showed sm1 infiltration.